what is Wireless transmission
antenna:
1.An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors
o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space
o Reception - collects electromagnetic energy from space
2.In two-way communication, the same antenna can be used for transmission and reception.
• G = antenna gain
• Ae = effective area
• f = carrier frequency
• c = speed of light (≈ 3 x 108 m/s)
• λ = carrier wavelength
o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space
o Reception - collects electromagnetic energy from space
2.In two-way communication, the same antenna can be used for transmission and reception.
Types of Antennas:
Isotropic antenna (idealized)
o Radiates power equally in all directions
Dipole antennas
o Half-wave dipole antenna (or Hertz antenna)
o Quarter-wave vertical antenna (or Marconi antenna)
Parabolic Reflective Antenna
o Used for terrestrial microwave and satellite applications
o Larger the diameter, the more tightly directional is the beam
People also ask by GOOGLE
Antenna Gain
Antenna gain
o Power output, in a particular direction, compared to that produced in any direction by a perfect omnidirectional antenna (isotropic antenna)
Expressed in terms of effective area
o Related to physical size and shape of antenna
Relationship between antenna gain and effective
area
• G = antenna gain
• Ae = effective area
• f = carrier frequency
• c = speed of light (≈ 3 x 108 m/s)
• λ = carrier wavelength
People also ask by GOOGLE
Propagation Modes
Ground-wave propagation
Sky-wave propagation
Line-of-sight propagation
Ground Wave Propagation:
back down to earth
Signal can travel a number of hops, back and
forth between ionosphere and earth’s surface
Reflection effect caused by refraction
Examples
o Amateur radio
o CB radio
o International broadcasts
Sky-wave propagation
Line-of-sight propagation
Ground Wave Propagation:
 |
| Ground Wave Propagation |
Ground Wave Propagation
Follows contour of the earth
Can Propagate considerable distances
Frequencies up to 2 MHz
Example
o AM radio
Sky Wave Propagation:
 |
| Sky Wave Propagation: |
Sky Wave Propagation
Signal reflected from ionized layer of atmosphereback down to earth
Signal can travel a number of hops, back and
forth between ionosphere and earth’s surface
Reflection effect caused by refraction
Examples
o Amateur radio
o CB radio
o International broadcasts
Line-of-Sight Propagation:
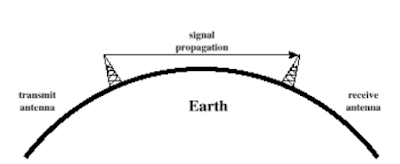 |
| Line-of-Sight Propagation: |
Line-of-Sight Propagation
Above 30 MHz neither ground nor sky wave propagation operates
Transmitting and receiving antennas must be within line of sight
o Satellite communication – signal above 30 MHz not
reflected by ionosphere
o Ground communication – antennas within effective line
of site due to refraction
Refraction – bending of microwaves by the atmosphere
o Velocity of electromagnetic wave is a function of the
density of the medium
o When wave changes medium, speed changes
o Wave bends at the boundary between mediums



إرسال تعليق
have you a any doubt then tell and if you want some topic then please tell .