Network Topologies:
• Topology - Physical and logical network
layout
– Physical – actual layout of the computer cables
and other network devices
– Logical – the way in which the network appears
to the devices that use it.
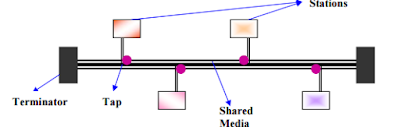
BUS Topology:
• Uses a trunk or backbone to which all of the computers on
the network connect.
• Systems connect to this backbone using T connectors or
taps.
• Coaxial cablings ( 10Base-2, 10Base5) were popular
options years ago
 |
| BUS |
 |
| advantages and disadvantsges |
People also ask by GOOGLE
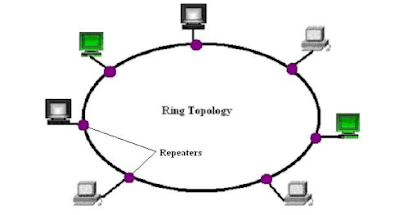
Ring Topology
• Logical ring
– Meaning that data travels in circular fashion
from one computer to another on the network.
– Typically FDDI, SONET or Token Ring
technology are used to implement a ring
network
– Ring networks are most commonly wired in a
star configuration
• Token Ring has multi-station access unit
(MSAU),equivalent to hub or switch. MSAU
performs the token circulation internally.
 |
| ring |
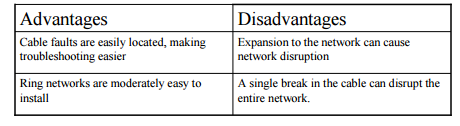 |
| ring advantages and disadvatages |
Star Topology:
• All computers/devices connect to a central
device called hub or switch.
• Each device requires a single cable
• point-to-point connection between the
device and hub.
• Most widely implemented
• Hub is the single point of failure
 |
| star topology |
 |
| advantages and disadvantages |
• Each computer connects to every other.
• High level of redundancy.
 |
| mesh topo |
• Rarely used.
– Wiring is very complicated
– Cabling cost is high
– Troubleshooting a failed cable is tricky
– A variation hybrid mesh – create point to point
connection between specific network devices, often
seen in WAN implementation.



Post a Comment
have you a any doubt then tell and if you want some topic then please tell .