DATA TRANSMISSION MODES
Transmission of digital data through a transmission medium can be performed either in serial or in parallel mode. In the serial mode, one bit is sent per clock tick, whereas in parallel mode multiple bits are sent per clock tick. There are two subclasses of transmission for both the serial and parallel modes, as shown in Fig
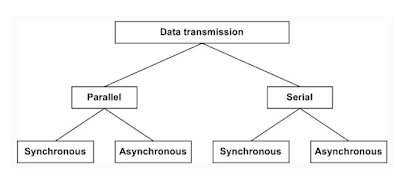 |
| Different modes of transmission |
Parallel Transmission
Parallel transmission involves grouping several bits, say n, together and sending all the n bits at a time shows.
how parallel transmission occurs for n = 8. This can be accomplishes with the help of eight wires bundled together in the form of a cable with a connector at each end. Additional wires, such as request (req) and acknowledgement (ack) are required for asynchronous transmission.
Primary advantage of parallel transmission is higher speed, which is achieved at the expense of higher cost of cabling. As this is expensive for longer distances, parallel transmission is feasible only for short distances.
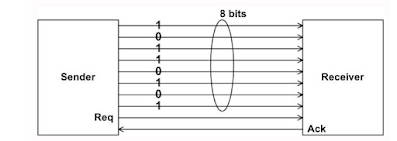 |
| Parallel mode of communication with n = 8 |
People also ask by GOOGLE
Serial Transmission
Serial transmission involves sending one data bit at a time. Figure shows how serial transmission occurs. It uses a pair of wire for communication of data in bit-serial form.
Since communication within devices is parallel, it needs parallel-to-serial and serial-to-parallel conversion at both ends.
Serial mode of communication widely used because of the following advantages:
•
Reduced cost of cabling: Lesser number of wires is required as compared to parallel connection
•
Reduced cross talk: Lesser number of wires result in reduced cross talk
•
Availability of suitable communication media
•
Inherent device characteristics: Many devices are inherently serial in nature
•
Portable devices like PDAs, etc use serial communication to reduce the size of the connector
However, it is slower than parallel mode of communication.
There are two basic approaches for serial communication to achieve synchronization of data transfer between the source-destination pair. These are referred to as – asynchronous and synchronous. In the first case, data are transmitted in small sizes, say character by character, to avoid timing problem and make data transfer self-synchronizing, as discussed later. However, it is not very efficient because of large overhead. To overcome this problem, synchronous mode is used. In synchronous mode, a block with large number of bits can be sent at a time. However, this requires tight synchronization between the transmitter and receiver clocks.
 |
| Serial mode of communication |
People also ask by GOOGLE
Direction of data flow:
There are three possible modes in serial communication: simplex, full duplex and half duplex
simplex:In simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, such as from a computer to a printer,
 |
simplex |
full-duplex:In full-duplex mode both the sides can communicate simultaneously, as shown in fig
 |
| full-duplex |
half-duplex :On the other hand, in half-duplex mode of communication, each station can both send and receive data, as shown in Fig.
 |
| half-duplex |


Post a Comment
have you a any doubt then tell and if you want some topic then please tell .