IP ADDRESSES :
ip is logical and unique address in networking. it is used for communicate over the internet without ip address we can not communicate over the internet.
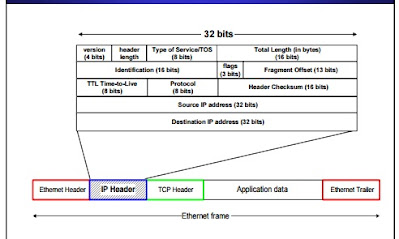 |
| IP PACKEST FORMETS |
An IP address
is a 32 bit long identifier
- encodes a network number (network prefix)
and a host number
Network prefix and host number
• The network prefix identifies a network and the host number
identifies a specific host (actually, interface on the network).
• How do we know how long the network prefix is?
– Before 1993: The network prefix is implicitly defined (see
class-based addressing)
or
– After 1993: The network prefix is indicated by a netmask
Dotted Decimal Notation:
• IP addresses are written in a so-called dotted decimal
notation
• Each byte is identified by a decimal number in the range
[0..255]
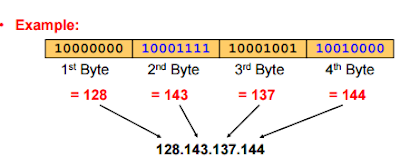 |
| dotted decimal notation |
Special IP Addresses:
• Reserved or (by convention) special addresses:
Loopback interfaces
– all addresses 127.0.0.1-127.0.0.255 are reserved for loopback interfaces
– Most systems use 127.0.0.1 as loopback address
– loopback interface is associated with name “localhost”
IP address of a network
– Host number is set to all zeros, e.g., 128.143.0.0
Broadcast address
– Host number is all ones, e.g., 128.143.255.255
– Broadcast goes to all hosts on the network
– Often ignored due to security concerns
• Test / Experimental addresses
Certain address ranges are reserved for “experimental use”. Packets should get dropped if
they contain this destination address (see RFC 1918):
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
• Convention (but not a reserved address)
Default gateway has host number set to ‘1’, e.g., e.g., 192.0.1.1




إرسال تعليق
have you a any doubt then tell and if you want some topic then please tell .